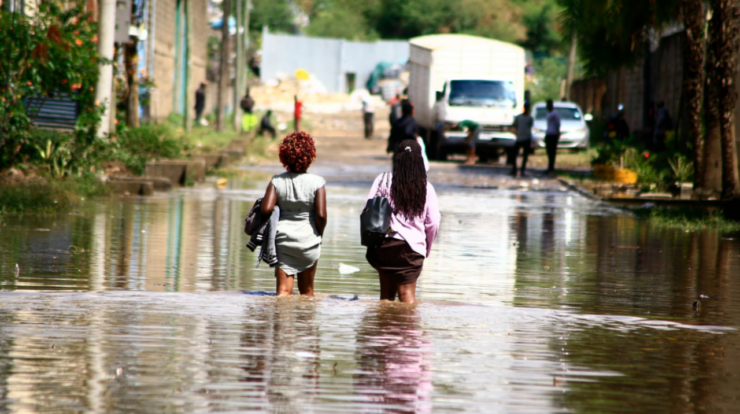
Kenya nairobi flooding – Nairobi, Kenya’s bustling capital, has become increasingly susceptible to devastating floods. A complex interplay of geographic factors, urbanization, and climate change has transformed the city into a flood-prone zone, posing significant challenges to its infrastructure, economy, and communities.
The city’s topography, characterized by low-lying areas and steep slopes, coupled with inadequate drainage systems, exacerbates flooding during heavy rainfall. Rapid urbanization has further compounded the problem, as impervious surfaces such as buildings and roads prevent rainwater from being absorbed into the ground.
Causes of Flooding in Nairobi, Kenya
Flooding in Nairobi, Kenya, is a persistent problem that has been exacerbated by urbanization and infrastructure development. The city’s geography also contributes to flooding, as it is located in a low-lying area prone to heavy rainfall.
Geographic Factors, Kenya nairobi flooding
Nairobi is situated on the banks of the Nairobi River, which flows through the city center. The city is also surrounded by hills, which can cause water to accumulate during heavy rainfall. In addition, Nairobi’s soil is composed of clay, which does not absorb water well.
Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
As Nairobi has grown, the city’s infrastructure has not been able to keep pace with the demand. This has led to the development of informal settlements, which are often built in flood-prone areas. In addition, the city’s drainage system is inadequate, which can cause water to accumulate during heavy rainfall.
Frequency and Severity of Flooding
Flooding in Nairobi has become more frequent and severe in recent years. In 2018, the city experienced its worst flooding in decades, which displaced over 100,000 people and caused billions of dollars in damage.
Impacts of Flooding in Nairobi, Kenya
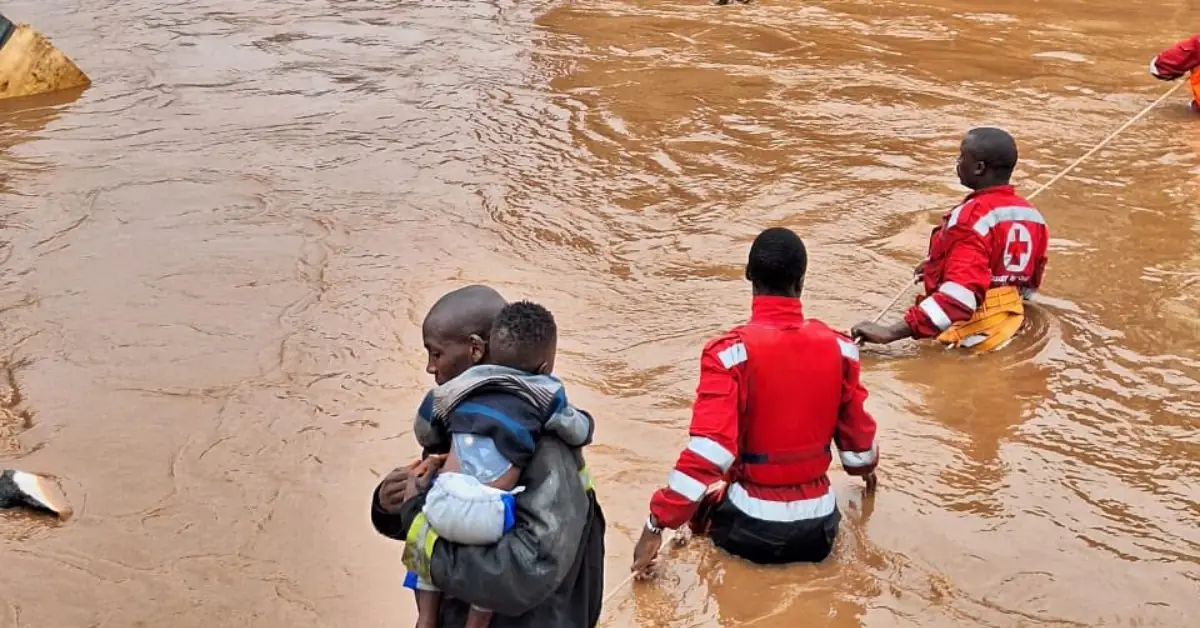

Flooding in Nairobi has a devastating impact on the city’s residents. The flooding can cause displacement, loss of life, and health risks.
Human Toll
- Displacement: Flooding can force people to leave their homes and seek shelter in temporary shelters or with friends and family.
- Loss of life: Flooding can cause drowning and other injuries.
- Health risks: Flooding can contaminate water sources and lead to the spread of waterborne diseases.
Economic Consequences
- Damage to infrastructure: Flooding can damage roads, bridges, and other infrastructure.
- Damage to businesses: Flooding can damage businesses and disrupt their operations.
- Damage to agriculture: Flooding can damage crops and livestock.
Social and Environmental Impacts
- Contamination of water sources: Flooding can contaminate water sources and make them unsafe for drinking.
- Disruption of ecosystems: Flooding can disrupt ecosystems and damage wildlife habitats.
Flood Mitigation and Management Strategies: Kenya Nairobi Flooding
There are a number of flood mitigation and management strategies that can be implemented in Nairobi. These strategies include:
Current Flood Control Measures
- Drainage systems: Nairobi has a drainage system that is designed to collect and remove rainwater from the city. However, the system is often inadequate, especially during heavy rainfall.
- Floodwalls: Nairobi has a number of floodwalls that are designed to protect the city from flooding. However, the floodwalls are not always effective, especially during heavy rainfall.
- Dams: Nairobi has a number of dams that are designed to control the flow of water into the city. However, the dams are not always effective, especially during heavy rainfall.
Effectiveness of Flood Control Measures
The effectiveness of flood control measures in Nairobi is limited. The drainage system is often inadequate, the floodwalls are not always effective, and the dams are not always effective. This is due to a number of factors, including the city’s geography, the lack of infrastructure, and the increasing frequency and severity of flooding.
Improvements to Flood Control Measures
There are a number of ways to improve the effectiveness of flood control measures in Nairobi. These include:
- Upgrading the drainage system: The drainage system in Nairobi needs to be upgraded to handle the increasing frequency and severity of flooding.
- Building new floodwalls: Nairobi needs to build new floodwalls to protect the city from flooding.
- Building new dams: Nairobi needs to build new dams to control the flow of water into the city.
Land-Use Planning and Sustainable Urban Development
Land-use planning and sustainable urban development can also help to reduce flood risk in Nairobi. Land-use planning can be used to identify areas that are at risk of flooding and to restrict development in these areas. Sustainable urban development can be used to create cities that are more resilient to flooding.
End of Discussion
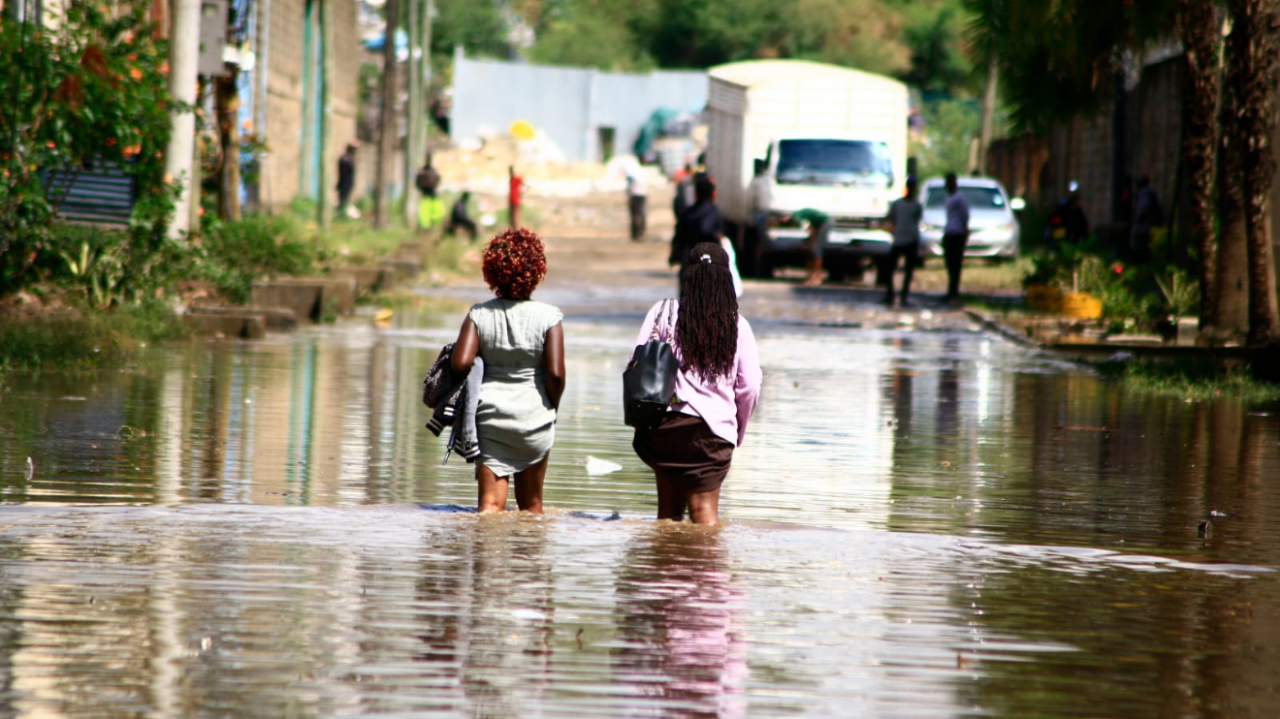

Addressing Nairobi’s flood woes requires a multi-faceted approach. Improving drainage infrastructure, implementing sustainable urban planning practices, and strengthening community resilience are crucial steps towards mitigating flood risks. Additionally, adapting to the impacts of climate change, such as changing rainfall patterns and rising sea levels, is essential for safeguarding the city’s future.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the main causes of flooding in Nairobi?
Nairobi’s floods stem from a combination of geographic factors, such as low-lying areas and steep slopes, coupled with inadequate drainage systems and rapid urbanization, which increases impervious surfaces.
How does climate change contribute to flooding in Nairobi?
Climate change exacerbates flooding in Nairobi through changing rainfall patterns, leading to more intense and frequent downpours. Additionally, rising sea levels pose a threat to low-lying coastal areas.
What are the impacts of flooding in Nairobi?
Flooding in Nairobi has severe consequences, including displacement of residents, loss of life, damage to infrastructure, disruption of businesses, contamination of water sources, and environmental degradation.